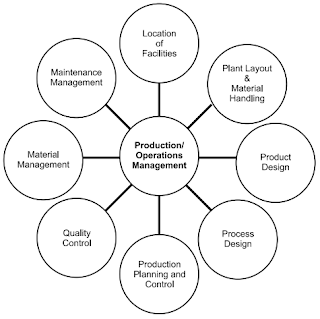
Production planning and control can be defined as the process of planning the production in advance, setting the exact route of each item, fixing the starting and finishing dates for each item, to give production orders to shops and to follow up the progress of products according to orders. The principle of production planning and control lies in the statement ‘First Plan Your Work and then Work on Your Plan’. Main functions of production planning and control includes planning, routing, scheduling, dispatching and follow-up.
Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it and who is to do it. Planning bridges the gap from where we are, to where we want to go. It makes it possible for things to occur which would not otherwise happen.
Routing may be defined as the selection of path which each part of the product will follow, which being transformed from raw material to finished products. Routing determines the most advantageous path to be followed from department to department and machine to machine till raw material gets its final shape.
Scheduling determines the programme for the operations. Scheduling may be defined as ‘the fixation of time and date for each operation’as well as it determines the sequence of operations to be followed.
Dispatching is concerned with the starting the processes. It gives necessary authority so as to start a particular work, which has already been planned under ‘Routing’and ‘Scheduling’. Therefore, dispatching is ‘release of orders and instruction for the starting of production for any item in acceptance with the route sheet and schedule charts’. The function of follow-up is to report daily the progress of work in each shop in a prescribed proforma and to investigate the causes of deviations from the planned performance.
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality Control (QC) may be defined as ‘a system that is used to maintain a desired level of quality in a product or service’. It is a systematic control of various factors that affect the quality of the product. Quality control aims at prevention of defects at the source, relies on effective feed back system and corrective action procedure.
Quality control can also be defined as ‘that industrial management technique by means of which product of uniform acceptable quality is manufactured’. It is the entire collection of activities which ensures that the operation will produce the optimum quality products at minimum cost.
The main objectives of quality control are:
- To improve the companies income by making the production more acceptable to the customers i.e., by providing long life, greater usefulness, maintainability, etc.
- To reduce companies cost through reduction of losses due to defects.
- To achieve interchangeability of manufacture in large scale production.
- To produce optimal quality at reduced price.
- To ensure satisfaction of customers with productions or services or high quality level, to build customer goodwill, confidence and reputation of manufacturer.
- To make inspection prompt to ensure quality control.
- To check the variation during manufacturing.
MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
Materials management is that aspect of management function which is primarily concerned with the acquisition, control and use of materials needed and flow of goods and services connected with the production process having some predetermined objectives in view.
The main objectives of materials management are:
- To minimise material cost.
- To purchase, receive, transport and store materials efficiently and to reduce the related cost.
- To cut down costs through simplification, standardisation, value analysis, import substitution, etc.
- To trace new sources of supply and to develop cordial relations with them in order to ensure continuous supply at reasonable rates.
- To reduce investment tied in the inventories for use in other productive purposes and to develop high inventory turnover ratios.
MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
In modern industry, equipment and machinery are a very important part of the total productive effort. Therefore, their idleness or downtime becomes are very expensive. Hence, it is very important that the plant machinery should be properly maintained.
The main objectives of maintenance management are:
- To achieve minimum breakdown and to keep the plant in good working condition at the lowest possible cost.
- To keep the machines and other facilities in such a condition that permits them to be used at their optimal capacity without interruption.
- To ensure the availability of the machines, buildings and services required by other sections of the factory for the performance of their functions at optimal return on investment.

This is a great and valuable article. Thanks for sharing and looking forward for reading more... Shams business setup
ReplyDeleteThanks for your feedback.
DeleteYour positive response highly appreciated.
Keep visit out site for more information
I was searching for the top Production Planning & Control. Thanks admin, for sharing such incredible content on this topic. Now I have got everything I need about it. Here’s another informative piece of content Sales & Distribution Management ERP. You may find more information here.
ReplyDelete